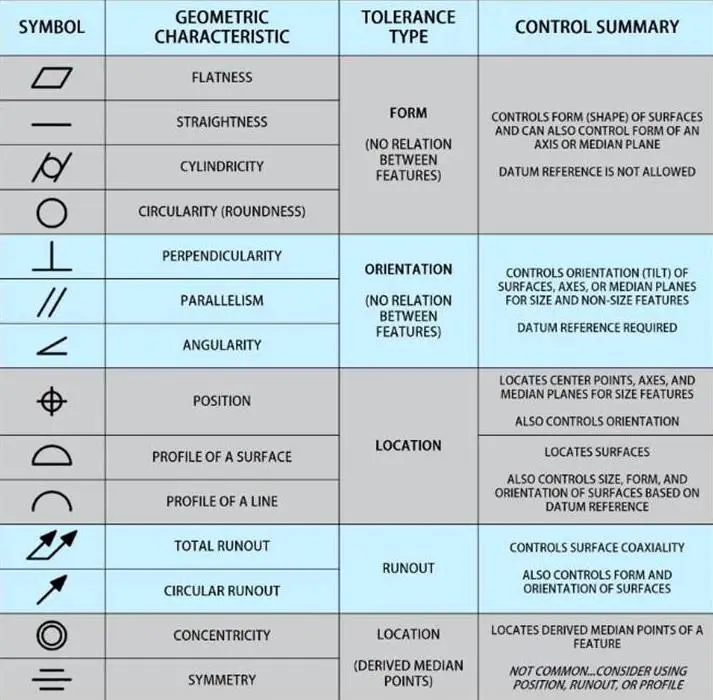
Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) symbols is a powerful technique for improving the precision and quality of manufactured parts. It’s used to communicate the design intent of engineers to manufacturers so that products can be made to precise specifications. One of the most important parts of GD&T is using the correct symbols to convey information accurately. If you’re in manufacturing or engineering, you’re likely familiar with GD&T symbols. We’ll examine some of the most common GD&T symbols and what they mean.
What Is GD&T?
Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) is a system specifying the form, shape, dimension, orientation, and location of features on mechanical parts. GD&T uses a set of standard symbols that clearly define these characteristics.
Why Use GD&T?
There are several reasons why engineers might use GD&T. First, GD&T can be used to specify the size and location of features with great precision. Second, GD&T can control the orientation of features, which is important for ensuring that parts fit together correctly. Finally, GD&T can ensure that features are symmetrical or evenly spaced apart.
Common system to explain the design intent
There are many benefits to using GD&T. First. It provides a common language that can be used to describe the design intent of a part. This is important for ensuring that the manufacturer understands the engineer’s vision for the final product. Second, GD&T is a very precise system, meaning that parts can be manufactured to tight tolerances. This is important for ensuring that the final product meets the customer’s expectations. Finally, GD&T can be used to create parts that are symmetrical or evenly spaced apart. This is important for creating a high-quality product.
Improves communication between engineers and manufacturers
Another benefit of GD&T is improving communication between engineers and manufacturers. Using GD&T symbols, engineers can communicate their design intent to the manufacturer. This can help ensure that the final product meets the customer’s expectations.
There are many benefits to using GD&T. It provides a common language that can be used to describe the design intent of a part, it is a very precise system, and it can be used to create parts that are symmetrical or evenly spaced apart. GD&T can also save money and time by reducing the need for rework or scrap. Finally, GD&T can improve communication between engineers and manufacturers.
What to Consider?
When considering whether or not to use GD&T, there are a few things to keep in mind. First, it is important to ensure that the engineer and the manufacturer are familiar with GD&T symbols. Second, GD&T can be used to create very precise parts. This means that the manufacturing process will need to be able to meet these tolerances. Finally, GD&T can add complexity to the engineering and manufacturing process. This means it is important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of using GD&T before deciding.
Intelligibility of the drawing
One of the most important things to consider when using GD&T is the intelligibility of the drawing. The GD&T symbols must be clear and easy to understand to avoid misunderstandings. This is especially important when communicating with the manufacturer.
The precision of the part
Another thing to consider is the precision of the part. GD&T is a very precise system, which means that the manufacturing process will need to meet these tolerances. This is especially important if the final product will be used in a critical application.
Cost and complexity
Finally, it is important to consider the cost and complexity of using GD&T. GD&T can add complexity to the engineering and manufacturing process. This means it is important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of using GD&T before deciding.
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Symbols
Many different GD&T symbols can be used to communicate information about a part. We will look at some of the most common GD&T symbols and what they mean.
Size Symbols
Several GD&T symbols can be used to indicate the size of a feature. The most common size symbol is the diameter symbol, which indicates the diameter of a circular feature.
The diameter symbol is a circle with two crossed lines in the centre. The diameter symbol is used to indicate the diameter of a circular feature.
Another common size symbol is the plus/minus symbol. This symbol is used to indicate the tolerance of a feature. The plus/minus symbol is two parallel lines with a space between them. The amount of space between the lines indicates the tolerance of the feature.
The third common size symbol is the angularity symbol. This symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be at a specific angle. The angularity symbol is a triangle with a line through the centre. The angularity symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be at a specific angle.
Location Symbols
There are several GD&T symbols that can be used to indicate the location of a feature. The most common location symbol is the true position symbol. The true position symbol is used to indicate the location of a feature in relation to its nominal position.
The true position symbol is a circle with a cross in the centre. The true position symbol is used to indicate the location of a feature in relation to its nominal position.
Another common location symbol is the datum target symbol. This symbol indicates the datum to which a feature is referenced. The datum target symbol is a circle with three crossed lines in the centre. The datum target symbol indicates the datum that a feature is referenced.
The third common location symbol is the profile of a line symbol. This symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be a specific distance from a datum. The profile of a line symbol is a line with two arrows at either end. The profile of a line symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be a specific distance from a datum.
Orientation Symbols
There are several GD&T symbols that can be used to indicate the orientation of a feature. The most common orientation symbol is the perpendicularity symbol. The perpendicularity symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be perpendicular to a datum.
The perpendicularity symbol is a line with a short vertical line at the end. The perpendicularity symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be perpendicular to a datum.
Another common orientation symbol is the parallelism symbol. This symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be parallel to a datum. The parallelism symbol is two lines with arrows at the end pointing in the same direction. The parallelism symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be parallel to a datum.
The third common orientation symbol is the angularity symbol. This symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be at a specific angle. The angularity symbol is a triangle with a line through the centre. The angularity symbol is used to indicate that a feature must be at a specific angle.
Conclusion
We hope this article has helped you understand some of the most common GD&T symbols and what they mean. As you can see, GD&T is a powerful technique for improving the precision and quality of manufactured parts. By using the correct symbols to communicate the design intent of engineers to manufacturers, products can be made to precise specifications. If you’re in the manufacturing or engineering fields, understanding GD&T symbols is essential to your work. Thanks for reading!